How to compare health insurance plans spreadsheet provides a practical, step-by-step approach to navigating the often-complex world of health insurance. This guide walks you through creating a customized spreadsheet to compare different plans, analyze coverage details, and evaluate provider networks, all leading to an informed decision.
This comprehensive resource dives deep into the intricacies of health insurance plan comparisons. From understanding different plan types like HMOs and PPOs to evaluating out-of-pocket costs and provider networks, this guide will equip you with the tools and knowledge to choose the right plan for your needs.
Understanding Health Insurance Plan Comparisons: How To Compare Health Insurance Plans Spreadsheet
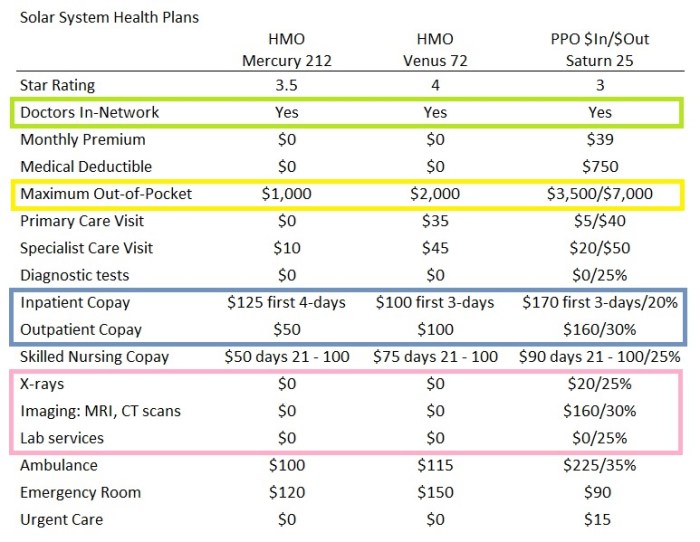
Health insurance plans vary significantly in their coverage and cost structures. Comprehending these differences is crucial for consumers to make informed decisions when selecting a plan that best meets their needs and financial situation. Careful comparison of plan features is essential to avoid unexpected out-of-pocket expenses.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
Health insurance plans are categorized into various types, each with distinct characteristics regarding network access, cost-sharing, and coverage specifics. Understanding these plan types is vital for effective comparison. Common types include Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), and Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs).
Key Factors for Plan Comparison
Several critical factors must be considered when evaluating health insurance plans. These factors encompass both coverage and cost elements, influencing the overall value proposition of a plan. Understanding these elements is paramount to selecting a plan that aligns with individual health needs and budget. Factors like deductibles, co-pays, coinsurance, and out-of-pocket maximums all contribute to the overall cost of care.
Plan Features: Deductibles, Co-pays, and Coinsurance
Deductibles, co-pays, and coinsurance are key cost-sharing components of health insurance plans. Deductibles are the amount a policyholder must pay out-of-pocket before the insurance company begins to pay. Co-pays are fixed amounts paid for specific services (e.g., doctor visits), while coinsurance is a percentage of the cost of a service that the policyholder is responsible for after the deductible has been met.
Understanding these features is critical for estimating the true cost of care under a specific plan.
Comparison of HMO, PPO, and EPO Plans
| Feature | HMO | PPO | EPO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network | Limited network of providers; requires referrals for specialists. | Wider network of providers; referrals are generally not required. | Wider network than HMOs but narrower than PPOs; referrals usually not required for specialists. |
| Cost-sharing | Generally lower premiums but potentially higher co-pays and deductibles for out-of-network care. | Generally higher premiums but lower co-pays and deductibles for out-of-network care. | Generally lower premiums than PPOs but potentially higher co-pays and deductibles for out-of-network care. |
| Flexibility | Least flexible; strict adherence to network providers is required. | More flexible; allows greater freedom to choose providers outside the network. | Moderately flexible; allows greater freedom to choose providers than HMOs but less than PPOs. |
| Out-of-Pocket Costs | Potentially lower out-of-pocket costs for in-network care. | Potentially higher out-of-pocket costs for in-network care. | Potentially moderate out-of-pocket costs for in-network care. |
Understanding Out-of-Pocket Costs
Out-of-pocket costs are the total amount a policyholder pays for healthcare services beyond what the insurance plan covers. This includes deductibles, co-pays, coinsurance, and other expenses. Careful consideration of out-of-pocket maximums is crucial, as they represent the upper limit of an individual’s potential expense under a specific plan. A thorough understanding of these costs helps to accurately assess the true financial burden of a plan.
For example, a plan with a high deductible might save money on premiums, but the policyholder might face a larger financial responsibility during a significant health event.
Creating a Spreadsheet for Plan Comparison
A crucial step in the health insurance selection process is the systematic comparison of different plans. A well-organized spreadsheet facilitates this comparison, allowing for a clear overview of key features and potential costs. This structured approach ensures a more informed decision-making process.A properly constructed spreadsheet template allows for a direct, side-by-side comparison of various plans. This approach is advantageous in identifying the best plan that aligns with individual needs and financial circumstances.
The spreadsheet approach also aids in identifying potential cost savings and ensures that the chosen plan meets the individual’s healthcare requirements.
Spreadsheet Template for Plan Comparison
A comprehensive spreadsheet template should include columns for essential plan details. This structured approach ensures clarity and ease of comparison. The following table provides a sample template.
| Plan Name | Provider | Deductible | Co-pay | Coinsurance | Network Coverage | Premium | Out-of-Pocket Maximum | Prescription Drug Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plan A | XYZ Insurance | $2,000 | $25 | 80/20 | Nationwide | $500 | $7,000 | Generic: $5, Brand Name: $15 |
| Plan B | ABC Insurance | $1,500 | $30 | 70/30 | Regional | $450 | $6,500 | Generic: $3, Brand Name: $10 |
Inputting Plan Data
Accurate data entry is crucial for reliable comparisons. Each plan’s specific details should be carefully recorded in the corresponding columns. This includes the provider, premium, deductible, co-pay, coinsurance, network coverage, out-of-pocket maximum, and prescription drug coverage details.
Calculating Estimated Out-of-Pocket Costs
To estimate out-of-pocket costs, consider potential scenarios. For instance, imagine a hypothetical scenario involving a doctor visit or prescription drug cost. These estimated costs can be calculated using the plan’s deductible, co-pay, and coinsurance details.
Estimated Out-of-Pocket Cost = Deductible + (Co-pay
- Number of Visits) + (Coinsurance
- Cost of Treatment)
For example, if a plan has a $1,500 deductible, a $25 co-pay, and 10 doctor visits, the estimated out-of-pocket cost for visits alone could be calculated as: $1,500 + ($25
- 10) = $1,750. Further, if a prescription drug costs $100 and the plan has 20% coinsurance, the additional cost is $100
- 0.20 = $20.
Highlighting Key Differences
The spreadsheet facilitates the identification of key differences between plans. Color-coding or using different formatting can highlight plans with lower premiums, higher network coverage, or lower out-of-pocket maximums. Using conditional formatting in spreadsheet software can help highlight these differences more easily. Comparing the data side-by-side, in a structured format, helps in the identification of differences in terms of cost, coverage, and network accessibility.
Comparing Plan Coverage
Comprehensive health insurance plans offer varying degrees of coverage for medical services, impacting the financial responsibility of the insured. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting a plan that aligns with individual needs and financial capacity. A detailed comparison of coverage options allows informed decisions regarding medical care and potential costs.
Coverage Options for Medical Services
Different plans offer various levels of coverage for medical services, encompassing preventive care, hospitalizations, and specialized treatments. In-network providers typically have lower out-of-pocket costs for services compared to out-of-network providers. Understanding the network of providers is a critical aspect of plan selection. Plans often have specific requirements for pre-authorization or referrals for certain procedures. This impacts the ability to receive care and the associated costs.
Comparing Coverage for Specific Medical Conditions or Procedures
Specific medical conditions or procedures may require unique considerations. Carefully review the plan documents for details regarding coverage limitations, exclusions, and specific costs. For example, a plan might have a specific limit on the number of physical therapy sessions covered for a back injury or a separate deductible for mental health services. Carefully examine the coverage details to understand how the plan will handle these scenarios.
Figuring out health insurance plans? A spreadsheet’s your best friend! List out all the plans, then compare costs and coverage. But if you’re looking for a new gig, check out available food industry jobs near you at jobs in the food industry near me. Once you’ve got that sorted, get back to comparing those insurance plans, focusing on the details that matter most for your needs.
You’ve got this!
Prescription Drug Coverage Options
Prescription drug coverage varies significantly between plans. This includes formularies (lists of covered drugs), co-pays, and cost-sharing arrangements. Some plans may require prior authorization for certain medications. This necessitates reviewing the formulary carefully to determine if the necessary medications are covered. Co-pay amounts and cost-sharing percentages can differ substantially, impacting the out-of-pocket expenses for prescription drugs.
Calculating Total Cost of a Medical Event
Calculating the total cost of a medical event under different plans requires a thorough analysis of various factors. This involves understanding deductibles, co-pays, co-insurance, and out-of-pocket maximums. A crucial component is understanding how the plan will handle out-of-network services. Using sample scenarios can help in determining the financial implications of different plans.
| Plan Name | Deductible | Copay (In-Network) | Estimated Total Cost (Example: Hospitalization) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plan A | $2,000 | $25 | $10,000 (including $2,000 deductible and $500 copay) |
| Plan B | $3,000 | $50 | $12,000 (including $3,000 deductible and $900 copay) |
| Plan C | $1,500 | $15 | $8,000 (including $1,500 deductible and $300 copay) |
Note: Estimated costs are examples and may vary based on specific circumstances.
Evaluating Provider Networks
Careful evaluation of provider networks is crucial when comparing health insurance plans. A plan’s network affects access to care, impacting the quality and convenience of healthcare services. Understanding the network’s composition, provider credentials, and coverage specifics is vital for making informed decisions. A robust network ensures timely and appropriate medical care, while a limited network may restrict choices and increase out-of-pocket costs.
Identifying Provider Network Characteristics
Comprehensive analysis of provider networks requires evaluating various key aspects. These aspects include the geographic reach of providers, their specialties, and the extent of in-network versus out-of-network coverage. Understanding these aspects enables a consumer to determine whether a plan aligns with their healthcare needs and preferences.
Evaluating Provider Location and Availability
Provider location and availability are significant factors. A plan’s network should ideally include providers located conveniently near the insured’s residence or workplace. Limited provider availability in a specific area can lead to challenges in accessing care promptly. Factors such as travel time and the distance to the nearest provider should be considered. This can be assessed by examining the geographic distribution of providers within the network.
Assessing Provider Credentials and Expertise
Evaluation of provider credentials and expertise is important for ensuring the quality of care. Reviewing providers’ board certifications, years of experience, and specialties is essential. This information can be found through online databases or directly from the provider’s profile. A comprehensive understanding of provider qualifications is crucial for choosing a plan that meets individual healthcare needs.
Comparing Specialist Availability
Specialist availability within the network is another crucial aspect. The presence of specialists in the network directly impacts access to specialized care, which is essential for complex medical conditions. Insured individuals should determine the availability of specialists in the plan’s network, considering their specific medical needs. Comparing the types of specialists available in different plans can aid in identifying the most suitable option.
Analyzing In-Network vs. Out-of-Network Coverage
Understanding in-network and out-of-network coverage is critical for evaluating the plan’s financial implications. In-network providers typically offer lower out-of-pocket costs for services. Out-of-network providers may result in higher costs, which can vary significantly depending on the plan and the provider. Evaluating the coverage structure and associated costs is essential for predicting potential financial burdens. The plan documents should explicitly detail the cost-sharing responsibilities for both in-network and out-of-network services.
Analyzing Out-of-Pocket Costs
Understanding the potential out-of-pocket costs associated with different health insurance plans is crucial for informed decision-making. This section details how to calculate these costs and the importance of various cost-sharing components. Accurate cost estimations empower individuals to select a plan that aligns with their financial capabilities and anticipated healthcare needs.
Calculating Potential Out-of-Pocket Costs
Determining the total out-of-pocket expenses for a health insurance plan requires a thorough understanding of several cost-sharing components. These elements, combined, create the overall financial responsibility for the insured individual. Careful consideration of these factors is essential to evaluate the true cost of a plan.
Significance of Deductibles, Co-pays, and Coinsurance
Deductibles, co-pays, and coinsurance are key cost-sharing mechanisms that directly influence the out-of-pocket expenses associated with healthcare services. Understanding how each of these components operates is critical to accurate cost estimation.
- Deductibles: A deductible is the amount an insured individual must pay out-of-pocket for covered healthcare services before the insurance plan begins to pay. The deductible amount varies significantly between plans, and this upfront cost is a crucial factor in initial financial planning.
- Co-pays: Co-pays are fixed amounts paid for specific healthcare services, such as doctor visits or prescription drugs. Co-pays are typically lower than deductibles, and they are generally predictable in cost.
- Coinsurance: Coinsurance is the percentage of covered healthcare costs that an insured individual is responsible for after meeting the deductible. This percentage is a consistent share of eligible expenses and is often a variable part of the overall cost.
Examples of Different Scenarios for Calculating Out-of-Pocket Expenses, How to compare health insurance plans spreadsheet
Different healthcare scenarios will result in varying out-of-pocket costs. To illustrate this, consider these examples.
Figuring out health insurance plans using a spreadsheet is a real brain twister. You gotta compare costs, coverage, and deductibles, right? Well, sometimes, you need a bit of extra protection like the mask of the sanguimancer face mask for a different kind of battle. But back to spreadsheets, you know, meticulously noting down all the details is key for choosing the best plan for your needs.
- Scenario 1: An individual with a $2,000 deductible incurs $1,500 in covered medical expenses before reaching the deductible threshold. Their out-of-pocket expense in this scenario is $1,500.
- Scenario 2: An individual with a $1,500 deductible incurs $2,500 in covered medical expenses. After meeting the deductible, they pay 20% coinsurance for the remaining $1,000, totaling $200 in coinsurance expenses. Their total out-of-pocket expense is $1,700 ($1,500 deductible + $200 coinsurance).
- Scenario 3: An individual with a $5,000 deductible has $1,000 in co-pays for doctor visits. Their out-of-pocket expense is $6,000 ($5,000 deductible + $1,000 co-pays).
Comparing Estimated Costs
To compare the estimated costs of different plans, a systematic approach is crucial. A spreadsheet is particularly effective for this comparison. By tracking deductibles, co-pays, and coinsurance rates, individuals can make an informed decision based on anticipated healthcare needs.
| Plan Name | Deductible | Co-pay (Doctor Visit) | Coinsurance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plan A | $2,000 | $25 | 20% |
| Plan B | $1,500 | $30 | 15% |
| Plan C | $5,000 | $20 | 30% |
A spreadsheet can organize these details, allowing for easy comparison of the total out-of-pocket costs across different plans, based on anticipated healthcare use.
Additional Considerations
Comprehensive health insurance plan comparisons necessitate a nuanced understanding beyond basic coverage details. Factors such as pre-existing condition handling, mental health provisions, preventive care incentives, customer service accessibility, and overall value proposition all significantly impact the long-term cost and benefit of a plan. A thorough assessment of these additional considerations empowers informed decision-making, ensuring a plan aligns with individual needs and circumstances.
Pre-Existing Conditions Coverage
Health insurance plans vary in their treatment of pre-existing conditions. Some plans may exclude coverage for conditions diagnosed prior to enrollment, potentially requiring a waiting period or imposing limitations on benefits. Others may cover pre-existing conditions from the outset, although this may be subject to certain limitations. Carefully review the plan documents to understand the specific stipulations for pre-existing conditions.
A key consideration is whether the plan requires a waiting period, and if so, the duration. Understanding these provisions is crucial for accurately evaluating the long-term affordability and reliability of the plan. Examples include plans that require a two-year waiting period for pre-existing conditions, or those that offer coverage without waiting periods.
Mental Health Services Coverage
Mental health services are an integral part of overall well-being, and their coverage under various health insurance plans warrants scrutiny. Plans may differ significantly in the types of mental health services covered, the frequency of visits allowed, and the provider networks available. Some plans may limit coverage to specific types of mental health professionals, while others offer broader access.
A comprehensive review of the plan’s mental health benefits, including the specific types of professionals covered, the frequency limits, and the geographic coverage of the provider network, is essential. For instance, some plans may cap the number of therapy sessions per year, or require prior authorization for certain services.
Preventive Care and Wellness Programs
Many plans now incorporate preventive care and wellness programs to promote proactive health management. These programs often provide incentives or discounts for preventative services like vaccinations, screenings, or health education resources. The extent of these programs can vary considerably among plans. The presence and value of these initiatives should be weighed against other potential costs and benefits.
Plans offering incentives for routine checkups or wellness programs may prove more cost-effective in the long run, particularly for those who prioritize preventative health.
Customer Service and Support Options
Effective customer service and support are critical for navigating claims, understanding coverage, and resolving issues. Assess the plan’s customer service channels, including phone numbers, email addresses, online portals, and available hours. The plan’s responsiveness and efficiency in handling inquiries or resolving claims can significantly impact the overall experience. A plan with multiple contact options and readily available customer service representatives might prove more valuable in times of need.
Overall Value Proposition
The overall value proposition of a health insurance plan encompasses more than just the cost and coverage. Consider factors such as the provider network’s breadth and depth, the plan’s out-of-pocket cost implications, and the quality of customer service. A plan’s perceived value is subjective and dependent on individual priorities. A comprehensive assessment should consider the total cost of care, including deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximums.
Compare the cost of the plan against the potential benefits and coverage provided. For example, a plan with a lower premium but a higher deductible might be a suitable option for those who anticipate minimal utilization of services, while a plan with a higher premium but a lower deductible might be preferable for those with a higher risk of requiring extensive care.
Using the Spreadsheet for Decision Making
The meticulously constructed spreadsheet serves as a crucial tool in the selection process of a suitable health insurance plan. By organizing key data points, the spreadsheet allows for a comprehensive and structured comparison of available plans. This structured approach enables a more informed and objective evaluation, minimizing the potential for emotional biases or overlooking critical factors.
Prioritizing Features and Benefits
Effective prioritization of features and benefits is essential for selecting a plan that aligns with individual needs. Factors such as coverage for specific medical conditions, preventive care services, and mental health benefits may differ significantly across plans. A well-organized spreadsheet facilitates the identification and comparison of these differences. For example, a person with a history of chronic conditions might prioritize plans with extensive coverage for those conditions.
Considering Personal Needs and Circumstances
Personal circumstances significantly impact the optimal choice of a health insurance plan. Factors such as age, family status, employment situation, and pre-existing medical conditions should be carefully evaluated. An individual with a young family may require a plan with higher coverage for pediatric care. Likewise, a person with a pre-existing condition should carefully examine plans’ coverage for that condition.
Analyzing these factors allows for a personalized approach to plan selection.
Long-Term Implications of Different Plans
Considering the long-term implications of different plans is crucial. While a plan might offer lower premiums initially, its long-term costs might increase significantly due to high out-of-pocket expenses or limited coverage. Analyzing the plan’s network of providers and out-of-pocket maximums will provide a comprehensive understanding of long-term implications. A thorough evaluation of these factors is critical for a sound financial decision.
For example, a plan with a lower premium but a higher deductible might seem attractive initially, but could lead to substantial out-of-pocket expenses if a major illness or injury occurs.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Plan Selection
A systematic approach to plan selection based on spreadsheet analysis is vital. This involves a series of steps to ensure a thorough and objective evaluation.
- Review Spreadsheet Data: Carefully examine all the data compiled on the spreadsheet, paying close attention to details like premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and coverage for specific procedures or conditions.
- Identify Priorities: Determine which features and benefits are most important based on personal needs and circumstances. This might involve assigning numerical weights to different factors, such as preventive care, mental health services, or coverage for specific medical conditions.
- Compare Plans: Analyze the spreadsheet data to compare plans side-by-side. Consider the total cost of each plan, including premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximums. Compare the provider networks and coverage for specific medical conditions.
- Assess Long-Term Implications: Evaluate the long-term financial implications of each plan. Estimate the potential out-of-pocket expenses and compare the total costs over a projected period. Consider potential changes in health status or financial circumstances that could affect the plan’s suitability.
- Make a Decision: Based on the analysis, select the plan that best meets individual needs and circumstances. This might involve consulting with a financial advisor or healthcare professional for further guidance.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, using a spreadsheet to compare health insurance plans empowers you to make an informed choice. By systematically evaluating coverage, costs, and provider networks, you can confidently select a plan that aligns with your individual health needs and financial situation. Remember to carefully consider all aspects before making your final decision.
FAQ Explained
What are the different types of health insurance plans?
Common types include HMOs (Health Maintenance Organizations), PPOs (Preferred Provider Organizations), and EPOs (Exclusive Provider Organizations). Each has unique characteristics regarding network coverage and cost-sharing.
How do I calculate estimated out-of-pocket costs?
Use the spreadsheet to input deductible, co-pay, and coinsurance amounts. Then, factor in potential medical expenses and consider scenarios with in-network and out-of-network services to estimate total costs.
How important is provider network coverage?
A strong provider network ensures access to doctors and specialists you need. Consider the availability of preferred specialists in your area and the plan’s in-network/out-of-network coverage details.
What are some tips for prioritizing plan features?
Prioritize features that directly address your healthcare needs, such as coverage for specific conditions or procedures. Consider your financial situation and long-term healthcare goals to weigh the features’ importance.
